An index is a systematic listing of the contents of a book, article, or other written work, arranged in alphabetical or chronological order to provide easy access to specific information. It is a valuable tool that allows readers to quickly locate the information they seek within a larger body of work.
Indexes are essential for organizing and retrieving information efficiently. They are widely used in books, encyclopedias, journals, and other publications to help readers navigate complex and extensive texts. Indexes can also be found in digital databases and online resources, providing quick access to specific information within vast amounts of data.
The creation of indexes has a long history, dating back to the ancient world. Early forms of indexes were used in libraries and archives to catalog and organize collections of documents. Over time, indexes evolved and became more sophisticated, playing a crucial role in the advancement of knowledge and scholarship.
- Kodiak Bluegill A Comprehensive Guide To The Majestic Fish Species
- Unveiling The Charm Of Booty Shorts Candid Moments
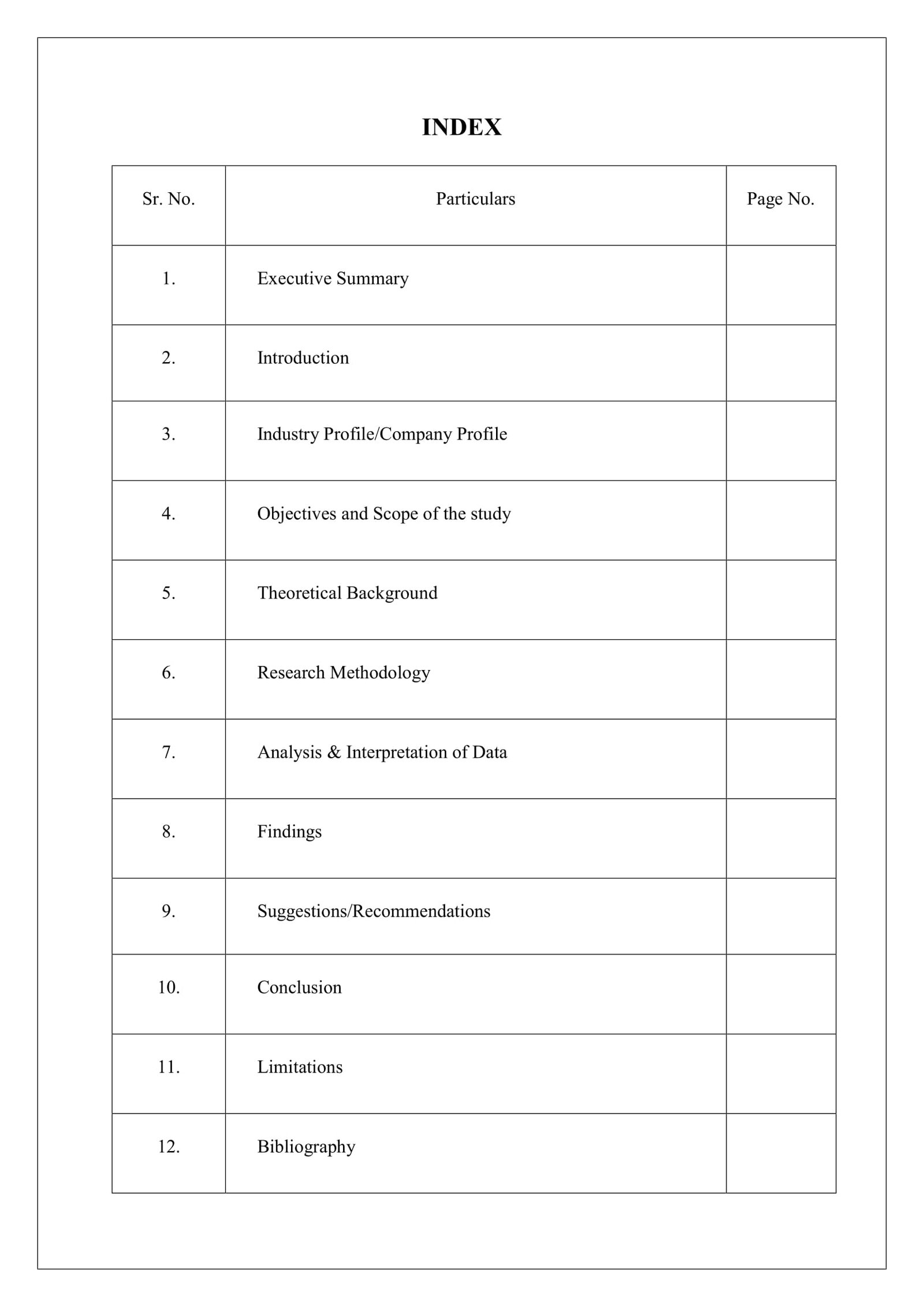
Index
An index is a crucial tool that organizes and presents information in a systematic manner. It enables efficient access to specific content within a larger body of work. The key aspects of an index encompass its various dimensions and functions:
- Organization: Indexes arrange content in a structured and logical order, making it easy to navigate.
- Retrieval: They facilitate quick and efficient retrieval of specific information within a text.
- Navigation: Indexes serve as a guide, helping readers locate relevant sections or pages.
- Comprehension: By providing an overview of the content, indexes enhance understanding of the overall structure and themes.
- Research: Indexes are indispensable for researchers, enabling them to pinpoint specific data or evidence.
- Cataloging: Indexes are used in libraries and archives to catalog and organize collections of documents.
- Data Management: They play a vital role in managing large amounts of data, providing efficient access to specific records.
- Digital Accessibility: Indexes are crucial for navigating digital content, allowing users to quickly find information on websites and online databases.
In conclusion, these key aspects highlight the multifaceted nature of indexes. They are essential tools for organizing, retrieving, and navigating information in various contexts, from books and articles to digital databases. By providing structured access to content, indexes empower readers, researchers, and professionals to efficiently locate the information they need.
Organization
The organizational aspect of indexes is a defining characteristic that greatly enhances their functionality and effectiveness. By arranging content in a structured and logical order, indexes provide a clear and systematic framework for users to navigate the information within a text.
- Exploring The Everglades Seal A Fascinating Marine Mammal
- Medium Knotless Braids With Curls A Comprehensive Guide To Achieve Stunning Lowmaintenance Hairstyles
- Facets:
An index typically consists of various facets, such as topics, keywords, authors, or dates, which are arranged alphabetically or chronologically. This organization allows users to quickly locate the specific information they seek without having to sift through the entire text.
- Components:
Each facet of an index comprises a list of entries, which include the specific terms or concepts being indexed. These entries are accompanied by page numbers or other references that guide users to the relevant sections within the text.
- Examples:
In a book index, the entries might represent specific topics covered in the book. In a journal index, the entries might represent article titles or authors. In a database index, the entries might represent records or data points.
- Implications:
The structured organization of indexes has several implications. First, it makes it easy for users to find the information they need quickly and efficiently. Second, it provides a comprehensive overview of the content, allowing users to identify relevant sections or pages without having to read the entire text.
In conclusion, the organizational aspect of indexes is crucial for their effectiveness. By arranging content in a structured and logical order, indexes empower users to navigate complex texts and locate specific information with ease.
Retrieval
The retrieval aspect of indexes is a fundamental component that underpins their value and usefulness. It refers to the ability of indexes to enable users to quickly and efficiently locate specific information within a text. This capability is achieved through a combination of structured organization and comprehensive listing.
Indexes provide a systematic framework for finding information by organizing content into specific facets, such as topics, keywords, authors, or dates. This organization allows users to navigate the index and pinpoint the relevant entries that lead them to the desired information within the text. The entries typically include page numbers or other references that guide users directly to the relevant sections.
The efficiency of indexes in facilitating retrieval is particularly important in large and complex texts, such as books, encyclopedias, and research papers. Without an index, users would have to manually search through the entire text, which could be time-consuming and frustrating. Indexes eliminate this challenge by providing a structured and targeted approach to finding specific information. This efficiency is crucial for researchers, students, and professionals who need to quickly locate specific data or evidence to support their work or studies.
In conclusion, the retrieval aspect of indexes is a critical component that enables users to quickly and efficiently locate specific information within a text. By providing a structured organization and comprehensive listing, indexes empower users to navigate complex texts and find the information they need with ease.
Navigation
The navigational aspect of indexes is closely tied to their overall functionality and effectiveness. As a guide, an index provides users with a structured and organized roadmap to navigate a text and locate relevant sections or pages. This navigational aid is particularly valuable in large and complex texts, such as books, encyclopedias, and research papers, where manually searching for specific information can be time-consuming and challenging.
Indexes achieve their navigational capabilities through their systematic organization and comprehensive listing. By arranging content into specific facets, such as topics, keywords, authors, or dates, indexes provide a clear and logical framework for users to follow. Each entry within a facet typically includes a page number or other reference that guides users directly to the relevant section of the text. This structured organization allows users to quickly and easily navigate to the specific information they seek, without having to read through the entire text.
The practical significance of the navigational aspect of indexes cannot be overstated. It empowers users to efficiently locate relevant information, saving them valuable time and effort. This efficiency is particularly important for researchers, students, and professionals who need to quickly access specific data or evidence to support their work or studies. Indexes serve as an indispensable tool for navigating complex texts and finding the information needed with precision and speed.
Comprehension
The comprehension aspect of indexes is closely tied to their role in providing an overview of the content within a text. This overview enhances the reader's understanding of the overall structure and themes, enabling them to grasp the key concepts and relationships within the text.
- Organization and Structure
Indexes provide a structured and organized representation of the content, reflecting the overall structure of the text. This organization allows readers to quickly identify the main sections, chapters, or topics covered in the text, helping them to understand the logical flow of information.
- Identification of Key Concepts
Indexes highlight the key concepts and themes discussed within the text. By listing specific terms, topics, or ideas, indexes help readers identify the most important aspects of the content, enabling them to focus their reading and comprehension.
- Contextual Understanding
Indexes provide context for the information presented in the text. By linking specific terms or concepts to their corresponding page numbers, indexes allow readers to quickly access the surrounding text, gaining a deeper understanding of the context in which those terms or concepts are discussed.
- Enhanced Navigation
The comprehension aspect of indexes is closely linked to their navigational capabilities. By providing an overview of the content, indexes enable readers to navigate the text more effectively, locating specific sections or passages that are relevant to their research or interests.
In conclusion, the comprehension aspect of indexes is a crucial element in enhancing the reader's understanding of the overall structure and themes of a text. Through their organized representation of content, identification of key concepts, provision of context, and enhanced navigation, indexes empower readers to grasp the essence of the text and engage with its content more deeply.
Research
The connection between research and indexes is profound and mutually reinforcing. Indexes are indispensable tools for researchers, providing a structured and efficient means to locate specific data or evidence within vast bodies of information. This capability is particularly crucial in academic research, where accuracy, precision, and efficiency are paramount.
Indexes play a pivotal role in accelerating the research process by enabling researchers to quickly and precisely identify relevant sources and data. Without indexes, researchers would face a daunting task of manually sifting through countless documents, books, and databases, a process that could be time-consuming and error-prone. Indexes eliminate this challenge by providing a comprehensive and organized listing of all the information contained within a text, allowing researchers to pinpoint the exact data or evidence they seek with ease.
The practical significance of this connection is evident in various research disciplines. For instance, in scientific research, indexes are essential for locating specific experimental data, research findings, and references. In historical research, indexes enable historians to quickly access primary sources, such as archival documents and historical records. Similarly, in legal research, indexes are indispensable for identifying relevant case laws, statutes, and legal precedents.
In conclusion, the connection between research and indexes is inseparable. Indexes serve as powerful tools that empower researchers to conduct their investigations with greater speed, accuracy, and efficiency. By providing a structured and organized framework for accessing specific data or evidence, indexes are indispensable components of the research process, enabling researchers to make significant contributions to their respective fields of study.
Cataloging
The connection between "Cataloging: Indexes are used in libraries and archives to catalog and organize collections of documents." and "index" lies in the fundamental role of indexes in organizing and providing access to vast collections of information. Cataloging is a critical process in libraries and archives, and indexes are indispensable tools for making these collections accessible to users.
Indexes provide a structured and systematic representation of the contents of a collection, enabling users to quickly and efficiently locate specific documents or information within the collection. Without indexes, navigating large collections would be a daunting and time-consuming task, as users would have to manually search through each document to find the information they need.
The practical significance of this connection is evident in various library and archival settings. For instance, in a university library, an index of the library's collection enables students and researchers to quickly locate books, articles, and other resources relevant to their research topics. Similarly, in a historical archive, an index of the archive's collection allows historians and researchers to quickly access primary sources, such as letters, diaries, and photographs, related to their historical inquiries.
The connection between "Cataloging: Indexes are used in libraries and archives to catalog and organize collections of documents." and "index" underscores the importance of indexes as essential tools for organizing and providing access to information. Indexes are not merely add-ons but integral components of libraries and archives, enabling users to navigate vast collections and locate the specific information they need with precision and efficiency.
Data Management
The connection between "Data Management: They play a vital role in managing large amounts of data, providing efficient access to specific records." and "index" is deeply rooted in the fundamental principles of data organization and retrieval. Indexes are essential components of effective data management systems, enabling users to quickly and accurately locate specific records within vast datasets.
In the context of data management, indexes serve as structured and searchable representations of data. They provide a mapping between data values and their physical storage locations, allowing for efficient access to specific records without the need to scan through the entire dataset. This is particularly crucial in large databases, where manual searching would be impractical or even impossible.
The practical significance of this connection is evident in various real-world applications. For example, in a customer relationship management (CRM) system, an index on the customer ID field enables quick retrieval of customer records based on their unique identifiers. Similarly, in a financial database, an index on the transaction date field allows for efficient filtering and retrieval of transactions within a specific time period.
Furthermore, indexes play a critical role in ensuring data integrity and consistency. By maintaining a synchronized mapping between data values and their storage locations, indexes help prevent data corruption and ensure the accuracy of data retrieval operations.
In summary, the connection between "Data Management: They play a vital role in managing large amounts of data, providing efficient access to specific records." and "index" underscores the importance of indexes as fundamental components of effective data management systems. Indexes enable efficient data retrieval, ensure data integrity, and support a wide range of real-world applications.
Digital Accessibility
The connection between "Digital Accessibility: Indexes are crucial for navigating digital content, allowing users to quickly find information on websites and online databases" and "index" lies in the fundamental role of indexes in organizing and providing access to information in digital environments. In the vast and ever-expanding world of online content, indexes serve as essential tools for users to efficiently locate the specific information they seek.
Indexes achieve this by creating structured representations of digital content, enabling users to search and retrieve information based on specific criteria. For example, on a website, an index might be used to organize and provide quick access to all the pages related to a particular topic or product. Similarly, in an online database, an index allows users to search for specific records based on fields such as author, title, or date.
The practical significance of this connection is evident in various real-world applications. For instance, in an e-commerce website, an index of product categories and subcategories enables users to quickly navigate and find the products they are interested in. In an academic research database, an index of article titles and abstracts allows researchers to efficiently identify and access relevant research papers.
Moreover, indexes play a crucial role in enhancing the accessibility of digital content for users with disabilities. By providing alternative ways to search and retrieve information, indexes empower users who may have difficulty navigating complex website structures or reading large blocks of text.
In summary, the connection between "Digital Accessibility: Indexes are crucial for navigating digital content, allowing users to quickly find information on websites and online databases" and "index" underscores the importance of indexes as essential components of effective digital content management. Indexes enable efficient information retrieval, enhance accessibility, and contribute to a more user-friendly and inclusive digital experience.
Index FAQs
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about indexes, offering valuable insights into their role and significance in various contexts.
Question 1: What is the primary purpose of an index?
An index serves as a systematic and organized listing of the contents of a text or collection, arranged alphabetically or chronologically. Its primary purpose is to provide quick and efficient access to specific information within a larger body of work, facilitating navigation and retrieval.
Question 2: How are indexes structured?
Indexes are typically structured into specific facets, such as topics, keywords, authors, or dates. Each facet consists of a list of entries that include the specific terms or concepts being indexed, along with corresponding page numbers or references that guide users to the relevant sections within the text.
Question 3: What are the key benefits of using an index?
Indexes offer several key benefits, including efficient retrieval of specific information, enhanced navigation through complex texts, improved comprehension of the overall structure and themes, and accelerated research processes by enabling researchers to quickly pinpoint relevant data or evidence.
Question 4: In what contexts are indexes commonly used?
Indexes find applications in a wide range of contexts, including books, articles, journals, encyclopedias, libraries, archives, and digital databases. They play a vital role in organizing and providing access to information across various disciplines and formats.
Question 5: How do indexes contribute to effective data management?
In data management systems, indexes serve as structured representations of data, providing a mapping between data values and their physical storage locations. This enables efficient access to specific records without the need to scan through the entire dataset, enhancing data retrieval speed and ensuring data integrity.
Question 6: How do indexes enhance digital accessibility?
In digital environments, indexes are crucial for navigating and retrieving information quickly and easily. They create organized representations of digital content, allowing users to search and access specific pages, articles, or records based on relevant criteria. This enhances the user experience and makes digital content more accessible, particularly for individuals with disabilities.
Summary: Indexes are indispensable tools for organizing, navigating, and retrieving information effectively. Their structured organization, comprehensive listing, and wide applications make them essential components in various contexts, including research, data management, and digital accessibility.
Transition: Having explored the fundamentals and benefits of indexes, let's delve into their historical evolution and the diverse applications they serve across different disciplines and domains.
Index Optimization Tips
To enhance the effectiveness and usability of indexes, consider implementing the following best practices:
Tip 1: Choose Relevant Keywords
Selecting appropriate keywords for indexing is crucial. Focus on terms that accurately represent the content and are likely to be used by users searching for information. Avoid overly broad or generic keywords that may lead to irrelevant results.
Tip 2: Use Consistent Terminology
Maintain consistency in the terminology used throughout the indexed content. Variations in spelling, capitalization, or abbreviations can fragment index entries and hinder effective retrieval. Establish clear guidelines for terminology usage.
Tip 3: Consider Context and Relationships
Indexes should not be limited to a mere listing of keywords. Incorporate contextual information and relationships between terms. This enhances the relevance and usefulness of the index, allowing users to navigate and discover information more effectively.
Tip 4: Prioritize Important Terms
Identify the most important terms or concepts within the indexed content and prioritize their placement in the index. This helps users quickly locate the most relevant information and improves the overall user experience.
Tip 5: Keep Indexes Updated
As the indexed content evolves, it is essential to regularly update the index to reflect the changes. Outdated or incomplete indexes can hinder the retrieval of accurate and up-to-date information.
Tip 6: Optimize for Digital Accessibility
In digital environments, ensure that indexes are optimized for accessibility. This includes providing alternative text for images, proper heading structures, and keyboard navigation options to cater to users with disabilities.
Summary: By implementing these optimization tips, you can create effective and user-friendly indexes that enhance the accessibility, relevance, and overall value of your content.
Transition: These tips provide a solid foundation for optimizing indexes. In the following section, we will explore the diverse applications of indexes across various domains and disciplines.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of "index," we have delved into its multifaceted nature and its profound impact on organizing, navigating, and retrieving information. Indexes have proven to be indispensable tools across various domains, empowering users to efficiently locate specific data, comprehend complex texts, and conduct research with precision.
As we move forward, the significance of indexes continues to grow in the digital age. With the ever-expanding volume of information available, effective indexing has become paramount for ensuring accessibility and usability. By embracing best practices and leveraging technological advancements, we can harness the full potential of indexes to unlock the wealth of knowledge and data at our fingertips.
- How To Archive Tiktok Videos A Comprehensive Guide
- Im Joking Im Joking A Comprehensive Dive Into The Art Of Humor And Wit