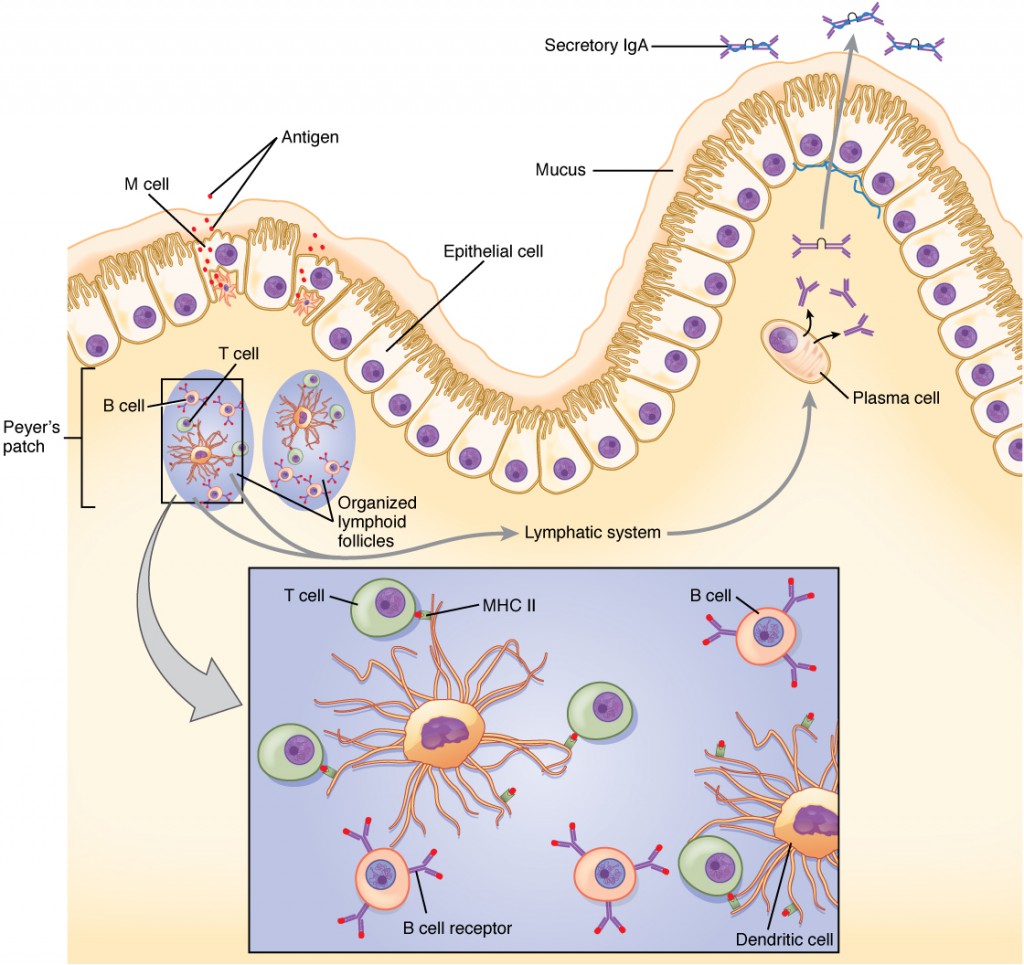
Peyer's patches are lymphoid tissues found in the small intestine. They help to protect the body from infection by trapping bacteria and other harmful substances. Peyer's patches are named after the Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer, who first described them in 1677. They are also known as aggregated lymphoid follicles.
Peyer's patches are located in the ileum, the last part of the small intestine. They are composed of clusters of lymphoid follicles, which are small, round structures that contain white blood cells. These white blood cells help to identify and destroy bacteria and other harmful substances. Peyer's patches are important for protecting the body from infection, especially during childhood when the immune system is still developing.
In addition to their role in protecting the body from infection, Peyer's patches also play a role in the development of the immune system. They help to educate the immune system to recognize and respond to different types of bacteria and other harmful substances. Peyer's patches are an important part of the body's immune system, and they play a vital role in protecting the body from infection.
- Sandia Tajin Costco A Refreshing Twist To Your Favorite Melon
- Megamind Mewing The Ultimate Guide To Transforming Your Jawline And Facial Structure
Peyer's Patches
Peyer's patches are lymphoid tissues found in the small intestine that play a crucial role in protecting the body from infection and aiding in the development of the immune system. Here are ten key aspects related to Peyer's patches:
- Location: Ileum (last part of small intestine)
- Structure: Clusters of lymphoid follicles
- Function: Trapping bacteria and harmful substances
- Role in immunity: Educating the immune system
- Development: Particularly important during childhood
- Size: Can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters
- Number: Typically 20-30 patches per person
- Peyer's patches are named after: Johann Conrad Peyer
- Other names: Aggregated lymphoid follicles
- Associated with: Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
In summary, Peyer's patches are essential components of the immune system, providing protection against infection and contributing to the development of immunological responses. Their unique location in the ileum and their ability to trap and identify harmful substances make them crucial for maintaining gut health and overall well-being.
Location
The location of Peyer's patches in the ileum, the last part of the small intestine, is crucial for their function and significance in the context of the immune system. Here are several key facets to consider:
- Funny Hinge Prompt Answers For Girls A Comprehensive Guide To Stand Out On The App
- Unveiling The Mystery Japaneat Face Reveal And The Story Behind The Iconic Persona
- Optimal exposure to antigens
The ileum is the site where a large number of antigens, or foreign substances, are encountered as food and other materials pass through the digestive tract. Peyer's patches are strategically positioned to capture and sample these antigens, allowing the immune system to mount an appropriate response. - Immune surveillance and regulation
The ileum is constantly exposed to both beneficial and harmful bacteria. Peyer's patches play a critical role in distinguishing between these microorganisms, promoting tolerance to harmless bacteria while initiating immune responses against pathogens. This immune surveillance helps maintain a healthy balance in the gut microbiome. - Induction of immune responses
Peyer's patches not only trap antigens but also contain specialized immune cells that process and present these antigens to other immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes. This process initiates and modulates immune responses, leading to the production of antibodies and the activation of other immune effector cells. - Interaction with gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
Peyer's patches are part of the larger network of lymphoid tissues in the gut known as GALT. They work in conjunction with other GALT components, such as mesenteric lymph nodes and isolated lymphoid follicles, to provide a comprehensive immune defense system for the gastrointestinal tract.
In summary, the location of Peyer's patches in the ileum is essential for their ability to monitor the gut environment, induce immune responses, and maintain immune homeostasis. This strategic positioning allows them to play a vital role in protecting the body from infection and ensuring the proper functioning of the immune system.
Structure
Peyer's patches are composed of clusters of lymphoid follicles, which are small, round structures that contain white blood cells. These white blood cells help to identify and destroy bacteria and other harmful substances. The unique structure of Peyer's patches allows them to perform their crucial functions within the immune system.
- Immune cell composition
Lymphoid follicles are composed of a variety of immune cells, including B cells, T cells, and macrophages. These cells work together to identify and eliminate pathogens. - Antigen presentation
Peyer's patches contain specialized cells called antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs capture and process antigens, displaying them on their surface. This allows other immune cells to recognize and respond to the antigens. - Germinal center formation
Within Peyer's patches, B cells undergo a process of maturation and differentiation within structures called germinal centers. Here, B cells proliferate and undergo genetic recombination, leading to the production of high-affinity antibodies. - Mucosal immunity
Peyer's patches are part of the mucosal immune system, which protects the body from pathogens at mucosal surfaces. The lymphoid follicles in Peyer's patches contribute to mucosal immunity by producing antibodies that can neutralize pathogens and prevent their entry into the body.
In summary, the structure of Peyer's patches, with their clusters of lymphoid follicles, enables them to fulfill their essential role in the immune system. Through the coordinated actions of various immune cells, Peyer's patches contribute to antigen presentation, immune cell activation, antibody production, and mucosal immunity.
Function
Peyer's patches play a vital role in protecting the body from infection by trapping bacteria and other harmful substances. They are located in the ileum, the last part of the small intestine, where they are exposed to a large number of antigens, or foreign substances.
Peyer's patches contain specialized lymphoid follicles that are rich in immune cells, including B cells, T cells, and macrophages. These cells work together to identify and destroy bacteria and other harmful substances. The lymphoid follicles in Peyer's patches are organized into a structure called a germinal center, where B cells undergo a process of maturation and differentiation. This process leads to the production of high-affinity antibodies, which are essential for protecting the body from infection.
The ability of Peyer's patches to trap bacteria and other harmful substances is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. Without Peyer's patches, the body would be more susceptible to infection. Peyer's patches are particularly important for protecting the body from food-borne infections.
Role in immunity
Peyer's patches play a critical role in educating the immune system. They help the immune system to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances, and they also help to develop immune tolerance. Immune tolerance is the ability of the immune system to not react to self-antigens, which are proteins that are found on the body's own cells. Without immune tolerance, the immune system would attack the body's own tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases.
Peyer's patches educate the immune system by presenting antigens to immune cells. Antigens are molecules that are recognized by the immune system as foreign. When an antigen is presented to an immune cell, the immune cell can either destroy the antigen or ignore it. Peyer's patches help to ensure that the immune system destroys harmful antigens while ignoring harmless antigens.
The education of the immune system by Peyer's patches is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. Without Peyer's patches, the immune system would be more likely to attack the body's own tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases.
Here is an example of how Peyer's patches educate the immune system: When a person eats a piece of food, the food is broken down into small molecules in the digestive tract. Some of these molecules are antigens that are recognized by the immune system. Peyer's patches sample these antigens and present them to immune cells. The immune cells then determine whether the antigens are harmful or harmless. If the antigens are harmful, the immune cells destroy them. If the antigens are harmless, the immune cells ignore them.
The education of the immune system by Peyer's patches is a complex process, but it is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. Peyer's patches help to protect the body from infection and autoimmune diseases.
Development
Peyer's patches undergo significant development during childhood, playing a vital role in shaping the immune system and providing protection against infections. Here are key aspects to consider regarding their development and importance during this period:
- Immune system maturation
During childhood, the immune system is rapidly maturing and developing its ability to recognize and respond to pathogens. Peyer's patches are actively involved in this process, providing a training ground for immune cells to encounter and learn from a wide range of antigens present in the gut environment. - Exposure to diverse antigens
Children are exposed to a vast array of antigens through food, environmental interactions, and vaccinations. Peyer's patches serve as a critical site for sampling and presenting these antigens to the immune system, facilitating the development of immune tolerance and the ability to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances. - Protection against infections
Peyer's patches are particularly important for protecting children against gastrointestinal infections, which are common during childhood. By trapping and eliminating pathogens in the gut, Peyer's patches help prevent the spread of infections and contribute to the overall health and well-being of the child. - Foundation for future immunity
The development of Peyer's patches during childhood lays the foundation for a robust immune system throughout life. The immune cells and immunological memory established during this period provide long-term protection against infections and contribute to overall health and disease resistance.
In summary, the development of Peyer's patches during childhood is crucial for the maturation of the immune system, exposure to antigens, protection against infections, and the establishment of a strong foundation for future immunity. Their importance underscores the need for proper nutrition, hygiene practices, and vaccination during childhood to support the optimal development and function of Peyer's patches.
Size
The size of Peyer's patches, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters, is a significant aspect related to their function and distribution within the small intestine. Here are key facets to explore:
- Variation in size and distribution
Peyer's patches exhibit variability in size and distribution along the length of the ileum. Smaller patches are typically found in the proximal ileum, while larger patches are more common in the distal ileum. This variation allows for efficient sampling of antigens throughout the small intestine. - Relationship to function
The size of Peyer's patches influences their functional capacity. Larger patches contain a greater number of lymphoid follicles and immune cells, enabling them to process and respond to a broader range of antigens. This contributes to the overall immune surveillance and protection provided by Peyer's patches. - Adaptation to changing conditions
The ability of Peyer's patches to vary in size is advantageous in adapting to changing conditions within the gut. During periods of increased exposure to antigens, such as during an infection, Peyer's patches can enlarge to enhance their immune response. Conversely, they can decrease in size when antigen exposure is reduced. - Implications for immune responses
The size and distribution of Peyer's patches impact the nature and effectiveness of immune responses. Larger patches facilitate more extensive interactions between immune cells and antigens, leading to robust immune responses. Smaller patches, while less efficient in antigen presentation, may contribute to immune tolerance by preventing excessive immune reactions.
In summary, the size of Peyer's patches is not merely a physical characteristic but has functional implications and contributes to the dynamic immune surveillance and response within the small intestine. Understanding the size variations and their significance enhances our comprehension of the role of Peyer's patches in maintaining gut health and overall immunity.
Number
The number of Peyer's patches in the human small intestine generally ranges from 20 to 30. This specific quantity and distribution are crucial for several aspects related to the function and effectiveness of Peyer's patches within the immune system.
- Immune surveillance optimization
The presence of multiple Peyer's patches along the length of the ileum optimizes the immune surveillance of the small intestine. Each patch acts as a sampling site for antigens, collectively providing a comprehensive monitoring system to detect and respond to potential pathogens or harmful substances. - Antigen diversity and exposure
The distribution of Peyer's patches ensures exposure to a wide range of antigens. Different regions of the small intestine encounter varying compositions of antigens, and the multiple patches allow for efficient capture and processing of these diverse antigens. - Immune cell collaboration
The presence of multiple Peyer's patches facilitates collaboration and communication among immune cells. Immune cells can migrate between patches, sharing information and coordinating immune responses. This inter-patch communication enhances the overall effectiveness of the immune system. - Redundancy and resilience
Having numerous Peyer's patches provides a level of redundancy in the immune defense system. If one patch is compromised or damaged, the other patches can compensate by increasing their activity and immune response, ensuring continuous protection against pathogens.
In summary, the number of Peyer's patches, typically ranging from 20 to 30, contributes to their optimal function in immune surveillance, antigen exposure, immune cell collaboration, and system resilience. This specific quantity and distribution are essential for maintaining a robust and effective immune response within the small intestine.
Peyer's patches are named after
The eponym "Peyer's patches" is a tribute to Johann Conrad Peyer, a renowned Swiss anatomist who first described these lymphoid structures in the small intestine in 1677. Peyer's meticulous observations and detailed illustrations laid the foundation for understanding the anatomy and significance of these immune-rich tissues.
Peyer's patches, also known as aggregated lymphoid follicles, are critical components of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which plays a vital role in protecting the body against ingested pathogens and maintaining intestinal homeostasis. The presence of Peyer's patches along the length of the ileum, the last portion of the small intestine, allows for efficient sampling and surveillance of luminal contents.
The naming of Peyer's patches after their discoverer underscores the importance of recognizing and acknowledging the contributions of scientists who advance our knowledge of human anatomy and physiology. This recognition not only honors Peyer's pioneering work but also highlights the significance of Peyer's patches in the context of mucosal immunity and overall health.
Understanding the connection between "Peyer's patches are named after: Johann Conrad Peyer" and "peyer ostrum" provides a deeper appreciation for the historical roots of medical terminology and the evolution of our understanding of the human body. It also emphasizes the critical role of scientific research and discovery in shaping our knowledge of health and disease.
Other names
The term "aggregated lymphoid follicles" is another name used to refer to Peyer's patches, highlighting their structural characteristics and functional significance within the mucosal immune system.
- Anatomical description
Peyer's patches are clusters of lymphoid follicles aggregated together in the ileum, the final portion of the small intestine. These follicles are composed of immune cells, primarily B cells and T cells, which play a crucial role in recognizing and responding to pathogens. - Immune function
As aggregated lymphoid follicles, Peyer's patches are central to the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which protects the intestinal mucosa from harmful microorganisms. They actively sample luminal antigens and initiate immune responses, either by directly eliminating pathogens or by presenting antigens to immune cells for further action. - Mucosal immunity
Peyer's patches contribute to mucosal immunity by producing antibodies, which are proteins that specifically bind to and neutralize pathogens. These antibodies can prevent pathogens from adhering to and invading the intestinal lining, thereby protecting against infections. - Immune regulation
In addition to their role in eliminating pathogens, Peyer's patches also participate in immune regulation. They contain specialized cells that can suppress immune responses, preventing excessive inflammation and maintaining immune homeostasis within the gut.
In summary, the use of the term "aggregated lymphoid follicles" to describe Peyer's patches emphasizes their anatomical structure, immune functions, and involvement in mucosal immunity and immune regulation. Understanding these aspects provides a comprehensive view of Peyer's patches and their critical role in maintaining intestinal health and overall well-being.
Associated with
Peyer's patches are closely associated with the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), a network of lymphoid tissues located throughout the gastrointestinal tract that plays a crucial role in mucosal immunity. Understanding the connection between Peyer's patches and GALT provides a comprehensive view of their function and significance within the immune system.
- Components of GALT
GALT encompasses various lymphoid structures, including Peyer's patches, isolated lymphoid follicles, and mesenteric lymph nodes. These components work together to provide a comprehensive immune defense system for the gastrointestinal tract. - Mucosal immunity
Peyer's patches, as part of GALT, are central to mucosal immunity, which protects the body from pathogens that enter through the digestive tract. They actively sample luminal antigens and initiate immune responses to eliminate pathogens and prevent their invasion. - Immune regulation
Peyer's patches contribute to immune regulation within GALT. They contain specialized cells that can suppress immune responses, preventing excessive inflammation and maintaining immune homeostasis in the gut. - Interconnections and communication
Peyer's patches are interconnected with other GALT components through lymphatic vessels. This network allows for the exchange of immune cells and information, facilitating coordinated immune responses throughout the gastrointestinal tract.
In summary, the association of Peyer's patches with GALT highlights their critical role in mucosal immunity and immune regulation within the gastrointestinal tract. Their integration into this network of lymphoid tissues enables a comprehensive and coordinated defense against pathogens and contributes to overall intestinal health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Peyer's Patches
Peyer's patches are lymphoid tissues located in the small intestine that play a critical role in the immune system. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about Peyer's patches:
Question 1: What is the function of Peyer's patches?Peyer's patches are responsible for trapping bacteria and other harmful substances in the small intestine, helping to protect the body from infection. They also play a role in the development of the immune system, educating it to recognize and respond to different types of bacteria and other harmful substances.
Question 2: Where are Peyer's patches located?Peyer's patches are located in the ileum, which is the last part of the small intestine.
Question 3: How many Peyer's patches does a person typically have?A person typically has between 20 and 30 Peyer's patches.
Question 4: Are Peyer's patches named after a person?Yes, Peyer's patches are named after Johann Conrad Peyer, a Swiss anatomist who first described them in 1677.
Question 5: What is the size of Peyer's patches?Peyer's patches can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Question 6: What is the significance of Peyer's patches being associated with GALT?Peyer's patches are associated with the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which is a network of lymphoid tissues located throughout the gastrointestinal tract. This association highlights their critical role in mucosal immunity, which is the body's defense system against pathogens that enter through the digestive tract.
Summary: Peyer's patches are important lymphoid tissues that play a crucial role in the immune system, particularly in protecting the body from infection and in the development of the immune system.
Transition to the next article section: To learn more about Peyer's patches and their function, please refer to the following article sections:
Tips Regarding Peyer's Patches
Peyer's patches are lymphoid tissues located in the small intestine that play a critical role in the immune system. Here are some important tips regarding Peyer's patches:
Tip 1: Maintain a Healthy Immune System
A healthy immune system is essential for Peyer's patches to function properly. Eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly can all help to boost your immune system and support the health of your Peyer's patches.
Tip 2: Get Vaccinated
Vaccines can help to protect you from infections that can damage Peyer's patches. Make sure to get vaccinated against common childhood diseases, such as measles, mumps, and rubella.
Tip 3: Practice Good Hygiene
Good hygiene can help to prevent the spread of bacteria and other harmful substances that can damage Peyer's patches. Wash your hands frequently, especially after using the bathroom or handling food. Avoid touching your face, and clean and disinfect surfaces that are frequently touched.
Tip 4: Eat a Healthy Diet
Eating a healthy diet is important for overall health, including the health of your Peyer's patches. Make sure to eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
Tip 5: Get Enough Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for overall health, including the health of your Peyer's patches. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
Summary: By following these tips, you can help to keep your Peyer's patches healthy and functioning properly. This will help to protect you from infection and other health problems.
Transition to the article's conclusion: Peyer's patches are an important part of the immune system. By following these tips, you can help to keep them healthy and functioning properly.
Conclusion
Peyer's patches are an essential component of the immune system, playing a critical role in protecting the body from infection. They are located in the small intestine and are composed of lymphoid follicles, which contain immune cells that help to identify and destroy bacteria and other harmful substances. Peyer's patches are also involved in the development of the immune system, helping to educate it to recognize and respond to different types of bacteria and other harmful substances.
Maintaining healthy Peyer's patches is important for overall health and well-being. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can help to keep your Peyer's patches healthy and functioning properly. This will help to protect you from infection and other health problems.
- Debra Bollman Stenographer Expertise Success And Professional Insights
- Tyler Funke The Rising Star In The Gaming Industry