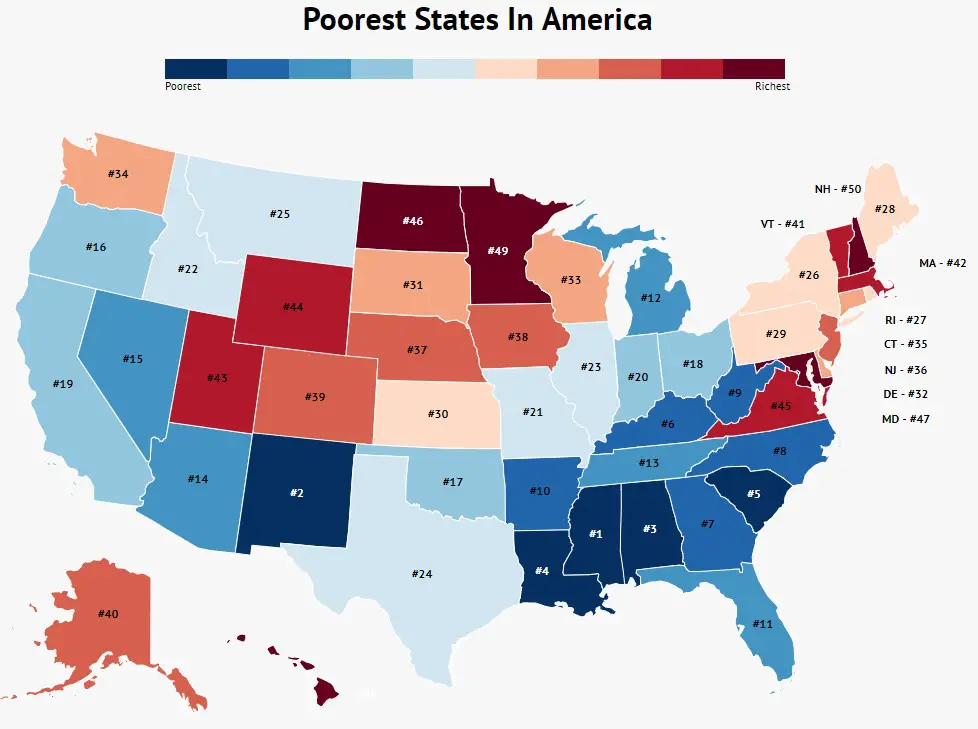
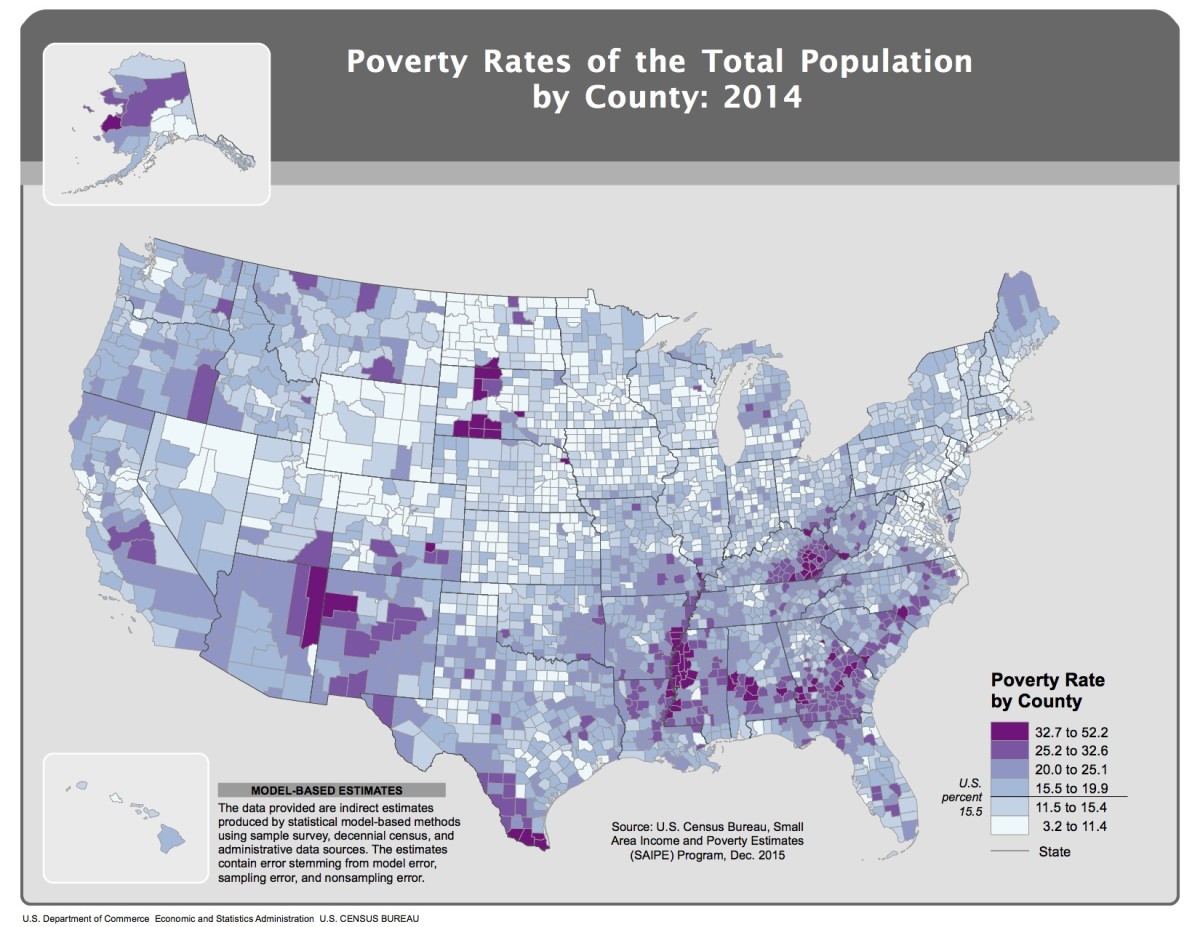
The term "poorest states" generally refers to states or regions with comparatively lower socioeconomic indicators and a higher prevalence of poverty among their populations. These states often face challenges related to economic development, job creation, and access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. Identifying the poorest states is crucial for policymakers and organizations working towards poverty alleviation and regional development.
Understanding the factors contributing to poverty in these states is essential for designing effective interventions and policies. Poverty can stem from various factors, including historical inequalities, lack of economic opportunities, limited access to education and healthcare, and inadequate infrastructure. Addressing these underlying issues is vital for promoting sustainable economic growth and improving the well-being of citizens in the poorest states.
This article will delve into the various dimensions of poverty in the poorest states, exploring the challenges they face and highlighting potential solutions and best practices for addressing these issues. We will examine the economic, social, and environmental factors that contribute to poverty and discuss strategies for promoting inclusive growth, creating job opportunities, and improving access to essential services in these regions.
- Vereena Motorcycle Accident A Comprehensive Analysis And Key Insights
- Debra Bollman Stenographer Expertise Success And Professional Insights
Poorest States
Understanding the poorest states requires a comprehensive exploration of various dimensions related to poverty and its underlying factors. Here are eight key aspects that shed light on this topic:
- Economic Indicators: Poverty rates, unemployment, income levels
- Social Factors: Education levels, healthcare access, crime rates
- Infrastructure: Transportation, housing, energy availability
- Historical Context: Historical inequalities, systemic racism, lack of opportunities
- Government Policies: Tax policies, social programs, public investments
- Environmental Factors: Climate change, natural disasters, environmental degradation
- Global Economic Trends: Globalization, trade patterns, economic crises
- Community Development: Local initiatives, non-profit organizations, grassroots movements
These key aspects are interconnected and influence each other to create the conditions that perpetuate poverty in certain states. For example, lack of economic opportunities and inadequate education can trap individuals in cycles of poverty, while poor infrastructure can hinder access to essential services and limit economic growth. Addressing these aspects requires a holistic approach that considers the historical, social, economic, and environmental factors that contribute to poverty in the poorest states.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators such as poverty rates, unemployment, and income levels play a crucial role in identifying and understanding the poorest states. These indicators provide quantifiable measures of the economic well-being of a state's population.
- Maduras Tetonas A Comprehensive Guide To Embracing Beauty And Confidence
- Monica Shoes Elevate Your Style With Comfort And Sophistication
- Poverty Rates: The poverty rate measures the percentage of a state's population living below the poverty line, which is a government-defined threshold of income necessary to meet basic needs. High poverty rates indicate a significant proportion of the population struggling to meet their basic needs, such as food, housing, and healthcare.
- Unemployment: The unemployment rate measures the percentage of the state's labor force that is unemployed. High unemployment rates indicate a lack of job opportunities and can lead to economic hardship, reduced income, and increased poverty.
- Income Levels: Median household income and per capita income provide insights into the overall economic well-being of a state's population. Low income levels can indicate a lack of economic opportunities, limited job growth, and disparities in wealth distribution.
- Income Inequality: Income inequality measures the distribution of income across a state's population. High income inequality indicates a significant gap between the wealthy and the poor, which can contribute to poverty and economic disparities.
These economic indicators are interconnected and provide a comprehensive view of the economic well-being of a state. They help identify areas where targeted interventions and policies are needed to address poverty and promote economic growth. By analyzing these indicators, policymakers can gain insights into the root causes of poverty and develop strategies to improve the economic conditions in the poorest states.
Social Factors
Social factors play a significant role in shaping the economic and social conditions of the poorest states. Education levels, healthcare access, and crime rates are key indicators of a state's overall well-being and can have a profound impact on poverty levels.
- Education Levels: Low education levels can perpetuate poverty by limiting economic opportunities and job prospects. Individuals with higher education are more likely to secure well-paying jobs, earn higher incomes, and contribute to economic growth. In the poorest states, improving education systems, increasing access to quality education, and promoting early childhood education are crucial for breaking the cycle of poverty.
- Healthcare Access: Lack of access to affordable and quality healthcare can lead to poor health outcomes, reduced productivity, and increased healthcare costs. In the poorest states, expanding Medicaid programs, increasing access to health insurance, and investing in community health centers are essential for improving the health and well-being of the population.
- Crime Rates: High crime rates can create a sense of insecurity, deter investment, and hinder economic development. In the poorest states, addressing crime requires a multifaceted approach that includes community policing, violence prevention programs, and investments in law enforcement and criminal justice reforms.
These social factors are interconnected and contribute to the cycle of poverty in the poorest states. By addressing these factors through targeted policies and interventions, it is possible to improve the overall well-being of the population, create a more just and equitable society, and ultimately reduce poverty rates.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure plays a crucial role in the economic and social development of any region, and its inadequacy can be a significant contributing factor to poverty in the poorest states. Transportation, housing, and energy availability are essential components of infrastructure that impact the lives of individuals and communities in numerous ways.
nadequate transportation infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and public transportation systems, can hinder access to jobs, education, healthcare, and other essential services. This can limit economic opportunities, particularly for low-income individuals who rely on public transportation or affordable housing near job centers. Poor housing conditions, such as overcrowding, lack of proper sanitation, and inadequate heating or cooling systems, can negatively impact health and well-being, leading to increased healthcare costs and reduced productivity.
Similarly, a lack of reliable and affordable energy access can pose significant challenges for households and businesses. In the poorest states, many communities lack access to reliable electricity, which can hinder economic development, limit access to technology and education, and impact the overall quality of life. Investing in infrastructure, including transportation, housing, and energy systems, is crucial for promoting economic growth, reducing poverty, and improving the well-being of residents in the poorest states. By addressing these infrastructural challenges, policymakers can create a more just and equitable society and lay the foundation for sustainable development.
Historical Context
The historical context of a region plays a significant role in shaping its present economic and social conditions. In the case of the poorest states, historical inequalities, systemic racism, and a lack of opportunities have created persistent barriers to economic growth and social mobility.
- Historical Inequalities: Centuries of discrimination and oppression have created deep-rooted inequalities in many of the poorest states. These inequalities have manifested in various forms, such as unequal access to education, healthcare, and housing. The legacy of slavery, Jim Crow laws, and other forms of systemic racism has created significant disparities in wealth, income, and opportunity between different racial and ethnic groups.
- Systemic Racism: Systemic racism refers to the ways in which racism is embedded in the institutions and policies of a society. This can take many forms, such as biased lending practices, discriminatory hiring practices, and unequal access to justice. Systemic racism has created barriers to economic advancement for people of color, making it more difficult for them to accumulate wealth, secure well-paying jobs, and build stable communities.
- Lack of Opportunities: Many of the poorest states have historically lacked the economic opportunities necessary to lift people out of poverty. This can be due to a lack of investment in infrastructure, education, and job creation. The absence of good-paying jobs, affordable housing, and quality education has made it difficult for residents of these states to improve their economic well-being.
- Intergenerational Poverty: Historical inequalities, systemic racism, and a lack of opportunities have created a cycle of intergenerational poverty in many of the poorest states. Children growing up in poverty are more likely to face challenges in education, health, and employment, which can perpetuate poverty across generations.
Understanding the historical context of poverty is crucial for developing effective policies and interventions to address the challenges faced by the poorest states. By acknowledging and addressing the root causes of poverty, it is possible to create a more just and equitable society where everyone has the opportunity to succeed.
Government Policies
Government policies, encompassing tax policies, social programs, and public investments, play a multifaceted role in shaping the economic and social landscape of the poorest states. These policies can have a significant impact on poverty rates, economic growth, and the overall well-being of residents.
- Tax Policies: Tax policies can influence the distribution of wealth and income within a state. Progressive tax systems, where higher earners pay a greater proportion of taxes, can help reduce income inequality and provide additional revenue for social programs aimed at reducing poverty.
- Social Programs: Social programs, such as Medicaid, food assistance, and housing assistance, provide a safety net for low-income individuals and families. These programs can help reduce poverty, improve health outcomes, and promote economic mobility. However, the adequacy and effectiveness of these programs can vary significantly from state to state.
- Public Investments: Public investments in education, infrastructure, and workforce development can create opportunities for economic growth and job creation. By investing in human capital and infrastructure, states can lay the foundation for long-term economic prosperity and reduce poverty.
- Intergovernmental Relations: The relationship between the federal government and state governments can also impact poverty levels in the poorest states. Federal funding for social programs and infrastructure projects can provide vital resources for these states. However, changes in federal policies or funding levels can have significant consequences for the poorest states.
The design and implementation of government policies are complex and often involve trade-offs between competing priorities. However, by carefully considering the impact of these policies on poverty and economic growth, states can develop a comprehensive approach to addressing the challenges faced by the poorest states.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as climate change, natural disasters, and environmental degradation are closely intertwined with poverty and economic development in the poorest states. These factors can exacerbate existing challenges and create new barriers to progress.
- Climate Change: Climate change is already having a significant impact on the poorest states, leading to more frequent and intense extreme weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. These events can cause widespread damage to infrastructure, disrupt livelihoods, and lead to food insecurity. In coastal areas, rising sea levels can also threaten homes and businesses, forcing residents to relocate and potentially increasing poverty rates.
- Natural Disasters: The poorest states are often more vulnerable to natural disasters due to a lack of adequate infrastructure and resources for disaster preparedness and response. When disasters strike, they can cause widespread damage and displacement, disrupting economic activity and exacerbating poverty.
- Environmental Degradation: Environmental degradation, such as air and water pollution, can also contribute to poverty in the poorest states. Poor environmental quality can lead to health problems, reduced agricultural productivity, and decreased tourism revenue. It can also make these states less attractive to businesses and investors, further hindering economic development.
- Interconnections: Climate change, natural disasters, and environmental degradation are often interconnected and can have cumulative impacts on the poorest states. For example, climate change can increase the frequency and intensity of natural disasters, while environmental degradation can make communities more vulnerable to these events.
Addressing environmental factors is essential for reducing poverty and promoting sustainable development in the poorest states. This includes investing in climate adaptation and resilience measures, strengthening disaster preparedness and response systems, and promoting sustainable practices that protect the environment and natural resources. By taking these steps, states can mitigate the impacts of environmental factors on their poorest residents and create a more just and equitable future.
Global Economic Trends
The global economy is a complex and interconnected system, and its trends can have a significant impact on the poorest states. Globalization, trade patterns, and economic crises are three key global economic trends that can affect poverty levels and economic development in these states.
- Globalization: Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness of the world's economies, cultures, and populations. While globalization can provide opportunities for economic growth and poverty reduction, it can also lead to increased inequality and job displacement in certain sectors. In the poorest states, globalization can have mixed effects, depending on their ability to integrate into the global economy and benefit from trade and investment.
- Trade Patterns: Trade patterns refer to the flow of goods and services between countries. Changes in trade patterns can have a significant impact on the poorest states, particularly those that are heavily dependent on exports of primary commodities. Fluctuations in global demand and prices for these commodities can lead to economic instability and poverty.
- Economic Crises: Economic crises, such as recessions or financial crises, can have a devastating impact on the poorest states. These crises can lead to job losses, reduced investment, and decreased trade, exacerbating poverty and inequality. The poorest states are often the most vulnerable to economic crises due to their limited economic resilience and lack of diversification.
Understanding the connections between global economic trends and poverty is essential for developing effective policies to promote economic growth and reduce poverty in the poorest states. By taking these trends into account, policymakers can design policies that mitigate the negative impacts of globalization, promote fair and equitable trade, and build resilience to economic crises.
Community Development
Community development plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges faced by the poorest states. Local initiatives, non-profit organizations, and grassroots movements are essential actors in fostering economic growth, promoting social justice, and empowering communities to overcome poverty.
- Local Initiatives: Local initiatives are community-led efforts that aim to address specific needs and challenges within a particular area. These initiatives can take various forms, such as community gardens, job training programs, and neighborhood watch groups. They play a vital role in building social capital, fostering a sense of community, and empowering residents to take ownership of their neighborhood's development.
- Non-profit Organizations: Non-profit organizations are mission-driven entities that provide a range of services to the poorest communities, including healthcare, education, housing assistance, and legal aid. These organizations often have deep roots in the communities they serve and are able to provide tailored support to meet the specific needs of the population. They play a critical role in filling gaps in public services and advocating for policies that promote social justice.
- Grassroots Movements: Grassroots movements are collective efforts that emerge from the community level to address systemic issues and advocate for change. These movements often focus on issues such as economic inequality, racial justice, and environmental protection. They play a vital role in raising awareness, mobilizing communities, and influencing policy decisions.
The collaboration between local initiatives, non-profit organizations, and grassroots movements is essential for creating lasting change in the poorest states. By working together, these actors can leverage their collective resources, expertise, and networks to address the root causes of poverty and promote sustainable development. Their efforts contribute to improving the quality of life for residents, fostering economic growth, and creating more just and equitable communities.
FAQs on Poorest States
Question 1: What are the common characteristics of the poorest states?
The poorest states often contend with a constellation of challenges, including high poverty rates, limited economic opportunities, inadequate infrastructure, and disparities in education, healthcare, and social services.
Question 2: What are the root causes of poverty in these states?
Poverty in the poorest states stems from a complex interplay of factors, encompassing historical inequalities, systemic racism, lack of economic opportunities, and inadequate access to essential services.
Question 3: What are the consequences of poverty for individuals and communities?
Poverty can have far-reaching consequences, affecting health outcomes, educational attainment, job prospects, and overall well-being. It can also perpetuate cycles of disadvantage across generations.
Question 4: What role does government play in addressing poverty?
Governments have a crucial role in mitigating poverty through policies that promote economic growth, expand access to education and healthcare, and provide social safety nets for the most vulnerable.
Question 5: How can individuals and organizations contribute to reducing poverty?
Individuals and organizations can support efforts to combat poverty through volunteering, donating to charities, advocating for policies that address the root causes of poverty, and promoting economic empowerment in disadvantaged communities.
Question 6: What are some promising strategies for reducing poverty in the poorest states?
Effective strategies for reducing poverty encompass investing in education and workforce development, expanding access to affordable housing and healthcare, promoting job creation through economic development initiatives, and addressing systemic inequalities.
By understanding the complexities of poverty in the poorest states and exploring potential solutions, we can contribute to creating a more just and equitable society for all.
Transition to the next article section: Challenges and Opportunities in Addressing Poverty in the Poorest States
Tips for Addressing Poverty in the Poorest States
Tackling poverty in the poorest states requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes of economic and social disparities. Here are five key tips to guide effective interventions:
Tip 1: Invest in Education and Workforce Development
Education is a powerful tool for breaking the cycle of poverty. By investing in early childhood education, K-12 schools, and job training programs, states can equip individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to secure good-paying jobs and achieve economic self-sufficiency.
Tip 2: Expand Access to Affordable Housing and Healthcare
Stable housing and access to quality healthcare are essential for families to thrive. States should implement policies that promote affordable housing options, expand Medicaid and other health insurance programs, and address the social determinants of health, such as food security and environmental quality.
Tip 3: Promote Job Creation through Economic Development
Job creation is crucial for reducing poverty. States should focus on attracting new businesses, supporting entrepreneurship, and investing in infrastructure projects that create employment opportunities. They should also work to improve the business climate and reduce regulatory barriers.
Tip 4: Address Systemic Inequalities
Systemic racism and other forms of discrimination perpetuate poverty. States should implement policies that promote equal opportunity in education, employment, housing, and the criminal justice system. They should also work to address the historical legacy of discrimination through restorative justice and reparations programs.
Tip 5: Foster Collaboration and Innovation
No single entity can solve the problem of poverty alone. States should foster collaboration among government agencies, non-profit organizations, businesses, and community groups. They should also encourage innovation and pilot programs that test new approaches to addressing poverty and its underlying causes.
By implementing these tips, the poorest states can make significant progress in reducing poverty and creating a more just and equitable society for all.
Transition to the article's conclusion: The Path Forward: Building a Brighter Future for the Poorest States
Conclusion
The issue of poverty in the poorest states is a complex and multifaceted one, deeply rooted in historical, economic, and social factors. Through this exploration, we have gained a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by these states and the strategies that can be employed to address them.
As we look towards the future, it is imperative that we remain committed to working collectively to create a more just and equitable society for all. By investing in education, expanding access to affordable housing and healthcare, promoting job creation, addressing systemic inequalities, and fostering collaboration, we can empower the poorest states to break the cycle of poverty and achieve lasting prosperity. The path forward may be challenging, but it is one that we must navigate together, ensuring that every individual has the opportunity to reach their full potential.
- Vereena Motorcycle Accident A Comprehensive Analysis And Key Insights
- Got It Wrong Outfits A Comprehensive Guide To Avoiding Fashion Mishaps