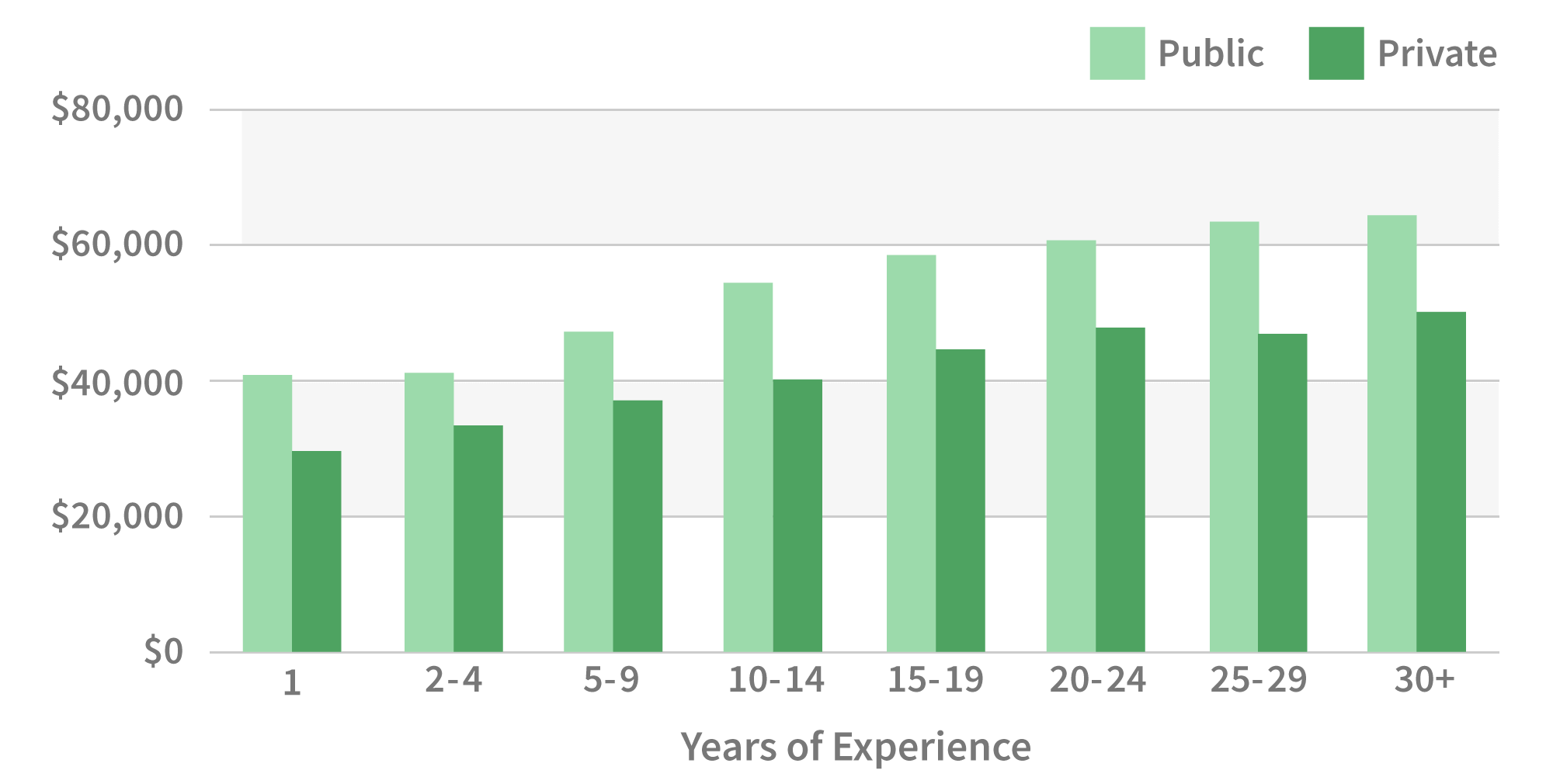
AP Teacher Salary refers to the compensation provided to educators who teach Advanced Placement (AP) courses in high schools. AP courses are college-level classes that allow students to earn college credit while still in high school.
AP teachers play a vital role in preparing students for higher education. They must have a deep understanding of their subject matter and be able to effectively communicate it to students. AP teachers also need to be able to create and maintain a positive learning environment.
The average AP teacher salary in the United States is \$64,350. However, salaries can vary depending on the state, school district, and experience of the teacher.
There are a number of benefits to teaching AP courses. AP teachers can earn higher salaries than teachers who do not teach AP courses. They also have the opportunity to work with motivated and engaged students. Furthermore, teaching AP courses can help teachers to develop their professional skills.
- Laios Feet Dungeon Meshi A Comprehensive Guide To Exploring The World Of Fantasy And Culinary Adventures
- How Tall Is Nle Choppa Exploring The Height And Legacy Of A Rising Music Icon
AP Teacher Salary
AP teacher salary is a critical component of the educational landscape, impacting the quality of education and the lives of students and educators.
- Competitive: AP teachers earn higher salaries than non-AP teachers, recognizing their specialized skills and contributions.
- Experience-based: Salaries increase with years of experience, rewarding teachers for their dedication and expertise.
- Location-dependent: Salaries vary geographically, influenced by cost of living and regional economic factors.
- Subject-specific: Compensation may differ based on the subject taught, reflecting market demand and teacher qualifications.
- School district policies: Salary schedules and benefits packages are determined by individual school districts, affecting teacher compensation.
- Professional development: Teachers who pursue professional development opportunities may qualify for salary increases.
- Performance-based pay: Some schools offer performance-based pay programs, linking salary to student outcomes.
- Negotiated contracts: Teacher unions and school districts negotiate contracts that determine salary and benefits packages.
- Cost of living adjustments: Salaries may be adjusted based on inflation and the rising cost of living.
- National averages: The average AP teacher salary in the United States provides a benchmark for comparison and analysis.
These key aspects highlight the multifaceted nature of AP teacher salary, influenced by factors such as experience, location, subject matter, and district policies. Understanding these aspects is essential for ensuring fair compensation, attracting and retaining qualified teachers, and ultimately supporting the success of AP programs and the students they serve.
Competitive
The competitive nature of AP teacher salaries is a direct reflection of the specialized skills and contributions that these educators bring to the classroom. AP teachers are responsible for delivering college-level instruction to high school students, preparing them for success in higher education.
- Unveiling Lawrence Sullivan A Comprehensive Guide To His Life Achievements And Legacy
- How Long Does Royal Honey Take To Work Unveiling The Secrets Of Natures Gift
- Advanced Curriculum: AP teachers must have a deep understanding of their subject matter and the ability to teach it at a college level. They must also be able to develop and implement lesson plans that are aligned with the College Board's rigorous standards.
- Student Engagement: AP teachers are skilled at engaging students in the learning process. They create a positive and challenging learning environment that encourages students to think critically and develop their problem-solving skills.
- Assessment Expertise: AP teachers are trained in the administration and scoring of AP exams. They are able to provide students with feedback on their performance and help them to improve their test-taking skills.
- Professional Development: AP teachers are committed to professional development. They regularly attend workshops and conferences to stay up-to-date on the latest teaching methods and content knowledge.
The specialized skills and contributions of AP teachers are essential to the success of AP programs. Their higher salaries are a recognition of the important role that they play in preparing students for college and beyond.
Experience-based
Within the context of "AP teacher salary," the experience-based salary structure holds significant relevance, recognizing the dedication and expertise that AP teachers accumulate over the course of their careers.
- Length of Service: As AP teachers gain experience, they develop a deeper understanding of their subject matter, pedagogical skills, and classroom management techniques. This increased proficiency contributes to their effectiveness as educators, benefiting students and the overall quality of AP programs.
- Professional Growth: Experienced AP teachers often engage in ongoing professional development activities, such as attending workshops, conferences, and pursuing advanced degrees. These endeavors enhance their knowledge and skills, enabling them to stay abreast of best practices and advancements in their field.
- Mentorship and Collaboration: With years of experience, AP teachers become valuable mentors to newer colleagues and student teachers. They provide guidance, support, and share their expertise, contributing to the professional growth of others.
- Institutional Knowledge: Experienced AP teachers accumulate a wealth of institutional knowledge about their school, district, and the AP program itself. This knowledge is invaluable in ensuring the smooth operation and continuous improvement of AP courses.
The experience-based salary structure for AP teachers serves as an incentive for educators to remain in the profession, invest in their professional development, and dedicate themselves to providing high-quality instruction to their students. By rewarding experience and expertise, schools and districts can foster a culture of excellence within their AP programs.
Location-dependent
The location-dependence of "AP teacher salary" is a crucial factor that shapes the compensation of these educators across different regions. This variation is primarily driven by two key elements: cost of living and regional economic factors.
- Cost of Living: The cost of living varies significantly from one location to another. In areas with a higher cost of living, such as major metropolitan centers, AP teachers tend to receive higher salaries to maintain a comparable standard of living. This adjustment ensures that these educators can afford housing, transportation, and other essential expenses in their respective communities.
- Regional Economic Factors: Regional economic factors, such as the strength of the local economy and the availability of jobs, also influence AP teacher salaries. In regions with a thriving economy and a high demand for qualified teachers, AP teachers may command higher salaries due to increased competition for their skills. Conversely, in areas with a weaker economy or an oversupply of teachers, salaries may be lower.
Understanding the location-dependence of "AP teacher salary" is important for several reasons. It allows AP teachers to make informed decisions about their careers, considering the financial implications of working in different locations. Additionally, it helps school districts and policymakers develop competitive salary schedules that attract and retain qualified AP teachers in their communities.
Subject-specific
The subject-specific nature of AP teacher salary is a significant factor that influences compensation within the profession. This variation is primarily driven by two key elements: market demand and teacher qualifications.
- Market Demand: The demand for AP teachers varies depending on the subject they teach. Subjects such as math, science, and English tend to have higher demand, as these are core subjects required for college admission and many careers. As a result, AP teachers in these subjects may receive higher salaries to attract and retain qualified educators.
- Teacher Qualifications: The qualifications required to teach AP courses also vary depending on the subject. Some subjects, such as physics and chemistry, require specialized knowledge and training, which may lead to higher salaries for qualified teachers.
- Teacher Experience: Experienced AP teachers in high-demand subjects, such as math and science, may command higher salaries due to their expertise and proven track record of success.
- School and District Policies: Some schools and districts may offer higher salaries for AP teachers in certain subjects to encourage enrollment and support student achievement in those areas.
Understanding the subject-specific nature of AP teacher salary is important for several reasons. It allows AP teachers to make informed decisions about their career paths, considering the earning potential of different subjects. Additionally, it helps school districts and policymakers develop competitive salary schedules that attract and retain qualified AP teachers in high-demand subjects.
School district policies
School district policies play a crucial role in determining AP teacher salary schedules and benefits packages. These policies vary from district to district, leading to differences in compensation for AP teachers across regions and states.
One of the key factors influenced by school district policies is the base salary for AP teachers. School districts set their own salary schedules, which determine the starting salary for teachers based on their education, experience, and credentials. These schedules may vary significantly between districts, resulting in different base salaries for AP teachers in different locations.
In addition to base salary, school districts also determine the structure of benefits packages for AP teachers. These benefits may include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and professional development opportunities. The availability and generosity of these benefits can impact the overall compensation package for AP teachers and influence their decisions about where to work.
Understanding the connection between school district policies and AP teacher salary is important for several reasons. For AP teachers, it is essential to research and compare salary schedules and benefits packages when considering job opportunities. By understanding the policies in different districts, AP teachers can make informed decisions about their careers and negotiate for fair compensation.
For school districts, it is crucial to develop competitive salary schedules and benefits packages to attract and retain qualified AP teachers. Recognizing the importance of AP teachers and investing in their compensation can help districts improve the quality of education for their students.
Professional development
The connection between professional development and AP teacher salary is significant, as professional development opportunities can lead to increased compensation. AP teachers who invest in their professional growth by attending workshops, conferences, and pursuing advanced degrees can enhance their skills and knowledge, making them more valuable to their schools and districts.
Professional development opportunities can help AP teachers stay up-to-date on the latest teaching methods and content knowledge in their subject areas. This advanced training can improve their effectiveness in the classroom, leading to improved student outcomes. As a result, schools and districts are more likely to reward AP teachers who pursue professional development with salary increases.
For example, a study by the National Board for Professional Teaching Standards found that teachers who earned National Board Certification, a prestigious recognition of teaching excellence, experienced an average salary increase of 10%. Similarly, a study by the American Federation of Teachers found that teachers who participated in high-quality professional development programs earned salaries that were 5% to 10% higher than those who did not participate.
Understanding the connection between professional development and AP teacher salary is essential for several reasons. First, it can help AP teachers make informed decisions about their careers and invest in their professional growth. By pursuing professional development opportunities, AP teachers can increase their earning potential and advance their careers.
Second, it can help schools and districts develop effective professional development programs that support AP teachers and improve student learning. By offering high-quality professional development opportunities, schools and districts can attract and retain qualified AP teachers and enhance the overall quality of education for their students.
Performance-based pay
Performance-based pay programs are increasingly being used to link AP teacher salary to student outcomes. These programs typically reward teachers for improving student performance on standardized tests, such as the AP exams. The goal of these programs is to incentivize teachers to focus on teaching the skills and knowledge that students need to succeed on these exams.
There is some evidence that performance-based pay programs can improve student outcomes. A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that a performance-based pay program in New York City led to a significant increase in student test scores. However, other studies have found no evidence that performance-based pay programs improve student outcomes.
There are a number of potential benefits to performance-based pay programs. First, these programs can help to ensure that teachers are focused on teaching the skills and knowledge that students need to succeed on AP exams. Second, these programs can provide teachers with an incentive to improve their teaching methods and strategies. Third, these programs can help to attract and retain high-quality teachers.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to performance-based pay programs. First, these programs can be complex and difficult to implement. Second, these programs can create incentives for teachers to teach to the test, rather than focusing on teaching the skills and knowledge that students need to succeed in college and beyond. Third, these programs can create a culture of competition among teachers, which can lead to a decrease in collaboration and teamwork.
Overall, the evidence on the effectiveness of performance-based pay programs is mixed. However, these programs have the potential to improve student outcomes and attract and retain high-quality teachers. It is important to carefully consider the potential benefits and drawbacks of these programs before implementing them.
Negotiated contracts
Negotiated contracts play a pivotal role in shaping AP teacher salary and benefits packages. Teacher unions, representing AP teachers, engage in collective bargaining with school districts to establish these contracts.
- Salary Schedules: Contracts outline salary schedules that determine AP teacher salaries based on factors such as experience, education level, and performance. These schedules provide a structured framework for salary increases and ensure fair compensation.
- Benefits Packages: Contracts also include provisions for benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and professional development opportunities. These benefits enhance the overall compensation package and contribute to AP teacher well-being and job satisfaction.
- Working Conditions: Contracts address working conditions, such as class size, teaching load, and support services. These provisions impact AP teachers' ability to deliver effective instruction and create a positive learning environment for students.
- Grievance Procedures: Contracts establish grievance procedures to address workplace concerns and disputes. These procedures protect AP teachers' rights and ensure fair treatment, contributing to a harmonious and respectful work environment.
Negotiated contracts are essential for ensuring fair compensation, comprehensive benefits, and supportive working conditions for AP teachers. They play a crucial role in attracting and retaining qualified AP teachers, ultimately benefiting students and the education system.
Cost of living adjustments
Cost of living adjustments play a critical role in determining AP teacher salary, ensuring that educators' compensation keeps pace with the rising cost of living and inflation. These adjustments are essential for maintaining the purchasing power and financial well-being of AP teachers.
When the cost of living rises, expenses such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare increase, eroding the value of fixed incomes. Cost of living adjustments aim to counterbalance this erosion by increasing salaries to maintain the same standard of living. This ensures that AP teachers can continue to afford basic necessities and maintain a comfortablewithout financial strain.
In practice, cost of living adjustments are typically tied to inflation rates. When inflation rises, salaries are adjusted upward to match the increased cost of goods and services. This process helps to preserve the purchasing power of AP teachers' salaries and ensures that they are fairly compensated for their work.
Understanding the connection between cost of living adjustments and AP teacher salary is crucial for several reasons. First, it highlights the importance of considering the cost of living when determining fair compensation for educators. Second, it underscores the need for regular salary adjustments to keep pace with inflation and maintain the financial well-being of AP teachers.
National averages
The national average AP teacher salary serves as a valuable reference point for understanding the compensation of these educators across the country. It provides a benchmark that allows for comparisons and analysis of salaries within different regions, districts, and subject areas.
- Regional Variations: Comparing the national average to regional salaries helps identify disparities in compensation across different parts of the country. This information can inform policy decisions aimed at addressing regional imbalances and ensuring equitable pay for AP teachers.
- District-Level Comparisons: School districts have the autonomy to set their own salary schedules, leading to variations in AP teacher salaries within a state. The national average provides a basis for evaluating the competitiveness of district salaries and making informed decisions about teacher recruitment and retention.
- Subject-Specific Analysis: The national average can also be used to analyze salary differences based on the subject taught. This information can help address potential disparities in compensation across different AP subject areas and ensure fair pay for all AP teachers.
- Historical Trends: Tracking changes in the national average salary over time provides insights into the overall trajectory of AP teacher compensation. This historical analysis helps identify trends, such as the impact of economic conditions or policy changes, on teacher salaries.
Understanding the connection between national averages and "ap teacher salary" is crucial for several reasons. It enables policymakers, school districts, and researchers to make informed decisions about teacher compensation, identify areas of concern, and develop strategies to attract and retain qualified AP teachers. The national average serves as a valuable tool for ensuring fair pay and supporting the provision of high-quality AP education for students across the United States.
FAQs about AP Teacher Salary
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about AP teacher salary, providing concise and informative responses to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What is the average AP teacher salary?
The average AP teacher salary in the United States is $64,350. However, salaries may vary depending on factors such as experience, location, subject taught, and school district policies.
Question 2: Do AP teachers earn more than non-AP teachers?
Yes, AP teachers typically earn higher salaries than non-AP teachers. This is because AP teachers have specialized skills and responsibilities, including teaching college-level curriculum and preparing students for AP exams.
Question 3: How does experience affect AP teacher salary?
Salaries for AP teachers increase with years of experience. This is because experienced teachers have developed a deeper understanding of their subject matter, pedagogical skills, and classroom management techniques.
Question 4: Does the location of the school impact AP teacher salary?
Yes, the location of the school can affect AP teacher salary. Salaries tend to be higher in areas with a higher cost of living, such as major metropolitan centers.
Question 5: Can AP teachers negotiate their salary?
In some cases, AP teachers may be able to negotiate their salary with their school district. However, salaries are typically determined by negotiated contracts between teacher unions and school districts.
Question 6: What is the job outlook for AP teachers?
The job outlook for AP teachers is expected to be good over the next few years. This is because there is a growing demand for qualified AP teachers, especially in high-demand subjects such as math, science, and English.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of key issues related to AP teacher salary. By understanding these factors, AP teachers can make informed decisions about their careers and advocate for fair compensation.
For further exploration, please refer to the next section of the article for additional insights and perspectives on "ap teacher salary."
Tips for Optimizing AP Teacher Salary
Maximizing your AP teacher salary requires a well-informed and strategic approach. Here are some practical tips to help you achieve your financial goals:
Tip 1: Research and Know Your Worth
Conduct thorough research on AP teacher salaries in your region and for your specific subject area. Utilize resources such as salary surveys, union contracts, and online databases to gather data. This knowledge empowers you to negotiate confidently and advocate for fair compensation.
Tip 2: Highlight Your Value and Experience
Quantify your accomplishments and emphasize your contributions to student success. Showcase your expertise in teaching AP curriculum, preparing students for exams, and fostering a positive learning environment. Highlight leadership roles, professional development initiatives, and any additional responsibilities you have taken on.
Tip 3: Explore Additional Compensation Opportunities
Inquire about opportunities for extra pay or stipends for additional responsibilities, such as club sponsorship, curriculum development, or a mentor to new teachers. Explore the possibility of summer teaching or online courses to supplement your income.
Tip 4: Seek Professional Development and Certifications
Investing in your professional growth can lead to salary increases. Pursue advanced degrees, attend workshops, and obtain certifications that enhance your skills and knowledge. These qualifications demonstrate your commitment to excellence and make you a more valuable asset to your school.
Tip 5: Network and Build Relationships
Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with other AP teachers. Building relationships with administrators, colleagues, and community members can provide valuable insights into salary trends and potential opportunities for career advancement.
Tip 6: Be Prepared to Negotiate
When negotiating your salary, be professional, well-prepared, and willing to compromise. Present your research and evidence to support your request. Be confident in your value, but also be realistic in your expectations.
Optimizing your AP teacher salary requires a proactive and strategic approach. By implementing these tips, you can increase your earning potential, enhance your professional standing, and continue to make a positive impact on the lives of your students.
Conclusion
The exploration of "ap teacher salary" reveals the multifaceted nature of educator compensation, influenced by a range of factors including experience, location, subject specialization, and district policies. AP teachers play a crucial role in preparing students for higher education, and their salaries should reflect the value they bring to the educational system.
Ensuring fair and competitive salaries for AP teachers is essential for attracting and retaining qualified educators, ultimately benefiting students and the future of education. By understanding the various elements that shape AP teacher salary, stakeholders can engage in informed discussions and work towards equitable compensation practices that recognize and support the vital contributions of these educators.
- Sandia Tajin Costco A Refreshing Twist To Your Favorite Melon
- Megamind Mewing The Ultimate Guide To Transforming Your Jawline And Facial Structure